Pemanasan induksi merupakan proses yang menggunakan prinsip induksi elektromagnetik untuk memanaskan benda. It is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, according to which when a conductor (usually a metal) is placed in a changing magnetic field, an electric current is induced, thereby producing heat.
How induction heat is produced
1. AC power supply: High-frequency AC power supply is usually used to generate changing magnetic fields. This power source generates a high-frequency alternating current through the coil, thereby creating an alternating magnetic field around the coil.
2. Generation of magnetic field: High-frequency alternating current flows in the coil to form an alternating magnetic field. This magnetic field will spread into the surrounding space.
3. Conductor placed in a magnetic field: The object to be heated, usually, a conductor (usually a metal), is placed in this alternating magnetic field. Due to changes in the magnetic field, arus listrik diinduksi di dalam benda.
4. Arus induksi menghasilkan panas: Menurut hukum induksi elektromagnetik Faraday, ketika fluks magnet pada konduktor berubah, arus induksi akan dihasilkan. Dalam hal ini, fluks magnet disebabkan oleh medan magnet bolak-balik, jadi arus induksi juga berubah seiring waktu. Arus induksi ini menciptakan hambatan di dalam konduktor, yang menghasilkan panas. Panas ini dapat digunakan untuk memanaskan konduktor itu sendiri atau dipindahkan ke benda lain yang bersentuhan dengan konduktor.
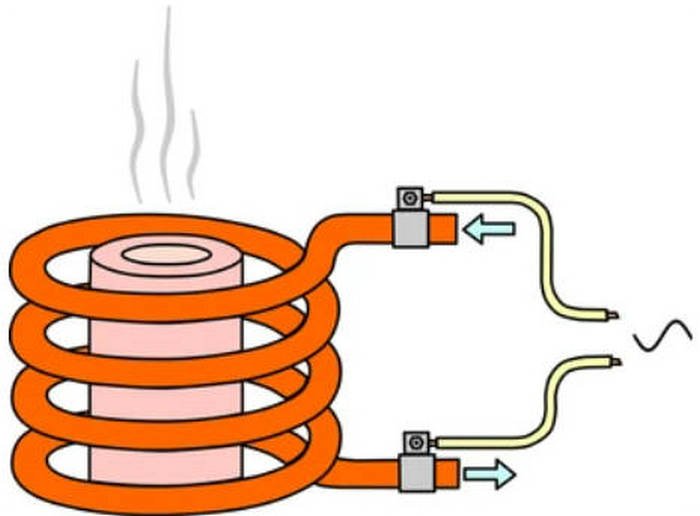
Dasar-dasar Pemanasan Induksi
1. Catu daya: Sistem pemanas induksi biasanya menggunakan daya AC frekuensi tinggi untuk menghasilkan arus bolak-balik frekuensi tinggi.
2. Gulungan: Kumparan adalah bagian dari catu daya dan digunakan untuk menghasilkan medan magnet bolak-balik frekuensi tinggi. Coil design and placement are critical to heating effectiveness.
3. Conductor: The object to be heated is usually a conductor, usually a metal. When a conductor is placed in an alternating magnetic field, an induced current is produced.
4. Induced current: The alternating magnetic field causes electrons inside the conductor to move, producing induced current. This induced current creates resistance in the conductor, yang menghasilkan panas.
5. Hysteresis loss:
Hysteresis losses occur in magnetic materials, such as ferromagnetic materials, when they are placed in an alternating magnetic field. This material undergoes a process of magnetization and demagnetization under the influence of a magnetic field, but this process is not completely reversible. When a magnetic material is periodically magnetized and demagnetized, energy loss occurs between the molecules and the magnetic domains, which is hysteresis loss. This loss causes the material to heat up, so it needs to be considered in applications such as induction heating.
6. Eddy current loss
Eddy current losses occur in conductors when they are exposed to alternating electromagnetic fields. Menurut hukum induksi elektromagnetik Faraday, an alternating magnetic field induces an induced current in a conductor. These induced currents create resistance inside the conductor and generate heat, which is eddy current loss. In induction heating, eddy current losses are often intentionally exploited because it is the primary mechanism used to heat the conductor.

Advantages of induction heating
Induction heating has many advantages and is therefore widely used in a variety of industrial, culinary and other applications.
1. Efficient energy conversion: Induction heating is an efficient heating method. Energi ditransfer dari sumber listrik ke benda kerja hampir tanpa energi yang terbuang, sehingga memungkinkan pemanfaatan energi yang lebih tinggi.
2. Pemanasan cepat: Pemanasan induksi dapat memanaskan benda kerja hingga mencapai suhu yang dibutuhkan dalam waktu yang sangat singkat. Hal ini membuat proses produksi lebih efisien dan mengurangi waktu tunggu.
3. Kontrol suhu yang tepat: Pemanasan induksi memungkinkan kontrol suhu benda kerja secara presisi karena pemanasan dapat dimulai atau dihentikan dengan cepat sesuai kebutuhan. Hal ini penting untuk aplikasi yang memerlukan kontrol suhu yang ketat, seperti perlakuan panas dan pengelasan.
4. Pemanasan seragam: Panas yang dihasilkan oleh pemanasan induksi didistribusikan secara merata ke seluruh benda kerja, sehingga masalah perlakuan panas atau deformasi yang tidak merata dapat dihindari.
5. Pemanasan non-kontak: Pemanasan induksi merupakan metode pemanasan non-kontak karena tidak memerlukan elemen pemanas yang bersentuhan dengan benda kerja, seperti pemanas api atau resistansi. Hal ini mengurangi risiko kontaminasi material dan kerusakan mekanis.
6. Dapat diotomatisasi dan terintegrasi: Pemanasan induksi dapat dengan mudah diintegrasikan dengan sistem otomatis, sehingga cocok untuk proses manufaktur industri bervolume tinggi. Itu bisa digunakan dengan robot, konveyor dan peralatan otomatis lainnya.
7. Menghemat energi dan biaya: Karena efisiensinya yang tinggi, pemanasan induksi dapat mengurangi konsumsi energi dan biaya pengoperasian, mengurangi biaya keseluruhan proses produksi.
8. Ramah lingkungan: Pemanasan induksi biasanya tidak melibatkan nyala api terbuka atau proses pembakaran, sehingga menghasilkan lebih sedikit polutan dan ramah lingkungan.
Induction heating is a flexible and efficient heating method suitable for a variety of industrial and non-industrial applications. It offers many advantages including efficient energy utilization, precise temperature control, pemanasan seragam, dll., making it one of the preferred heating technologies in many industries.
Does coil design matter in induction heating systems?
Coil design is very important in induction heating systems because the coil is one of the key components of induction heating, which directly affects heating efficiency, heating uniformity and system performance. The following is the importance of coil design in induction heating systems:
1. Efisiensi pemanasan: The design of the coil affects the efficiency of energy transfer. The optimized coil design ensures that as much electromagnetic energy as possible is transferred to the workpiece, sehingga meningkatkan efisiensi pemanasan. Desain koil yang efisien juga mengurangi pemborosan energi dan menurunkan biaya pengoperasian.
2. Keseragaman pemanasan: Bentuknya, ukuran dan posisi kumparan akan mempengaruhi keseragaman pemanasan benda kerja. Desain kumparan yang tepat memastikan distribusi suhu yang seragam di dalam benda kerja dan menghindari titik panas dan dingin. Hal ini penting untuk aplikasi yang memerlukan kontrol suhu yang tepat, seperti perlakuan panas.
3. Pemilihan frekuensi: Desain kumparan yang berbeda dapat digunakan untuk menghasilkan medan elektromagnetik dengan frekuensi berbeda. Pemilihan frekuensi kumparan tergantung pada bahan dan ukuran benda kerja, serta kedalaman pemanasan yang dibutuhkan. Pemilihan frekuensi yang tepat membantu mengoptimalkan efek pemanasan.
4. Daya tahan kumparan: Kumparan harus dirancang untuk tahan terhadap suhu tinggi, high frequency and high current environments. Appropriate coil materials and structural design can ensure stable operation of the coil for a long time and reduce maintenance costs.
5. System integration: Coil design also needs to consider how to integrate with the entire induction heating system. This includes the coil’s cooling system, power connections and control systems, dll.. Coils must work in harmony with other components to ensure proper operation of the system.
Overall, coil design is critical to the performance and stability of your induction heating system. Optimized coil design can improve heating efficiency, heating uniformity and system reliability to adapt to different application needs, including industrial production, perawatan panas, pengelasan, medical equipment and food heating, dll.. Karena itu, coil design is often an important consideration in the design and optimization of induction heating systems.
Applications of induction heating
Induction heating is a heating technology widely used in various industrial and non-industrial fields. It transfers energy into conductive materials through the principle of electromagnetic induction, thereby heating objects. Here are some of the main application areas for induction heating:
1. Industrial heating: Induction heating is widely used in industrial production to heat metal and non-metallic materials for various processes, including forging, pendinginan, perawatan panas, crucible melting, mematri, thermal welding, metal hot pressing, dll.. It is commonly used to heat parts, bearings, gears, pipes and other industrial components.
2. Medical equipment: In the medical field, induction heating is used to generate high-frequency electromagnetic fields to heat tissues for physical therapy, such as high-frequency hyperthermia and electromagnetic induction heating therapy.
3. Food heating: Induction heating is used in the food industry to quickly heat food and liquids, such as induction heating furnaces and induction heating stoves. This method heats food quickly, improving production efficiency while reducing the risk of overheating and burning the food.
4. Aerospace: Induction heating is used in the aerospace field, including the heating and heat treatment of aircraft engine parts to improve material performance and durability.
5. Automobile Manufacturing: In automobile manufacturing, induction heating is used in a variety of applications, including welding, thermoforming, quenching and surface treatment, to improve the performance and quality of parts.
6. Electronic Manufacturing: Induction heating is used in the manufacture of semiconductor equipment, circuit boards and electronic components in electronic manufacturing to ensure high precision and performance.
7. Metallurgy: In the metallurgical industry, induction heating is used in metal smelting, casting and alloy preparation to obtain the desired metal properties.
8. Home appliances: Induction heating is also used in home appliances, such as induction heating stoves, induction heating kettles and induction heating cookers, to improve cooking efficiency and safety.
In general, induction heating is an efficient, precise and widely applicable heating technology. It has important applications in many fields and helps to increase production efficiency, improve product quality and save energy.

Power requirements
The power requirements of induction heating systems are critical because they directly affect heating efficiency and system performance. The following are the main aspects of power requirements for induction heating systems:
1. High-frequency AC power supply: Induction heating usually requires high-frequency AC power supply, with the frequency usually ranging from thousands of hertz (Hz) to hundreds of kilohertz. This is because high-frequency AC power effectively induces currents in conductors, thereby generating heat.
2. Power requirements: The power requirements of the power supply depend on the application of the induction heating system and the size of the workpiece. Large industrial induction heating systems may require thousands of kilowatts (kW) or even megawatts (MW) of power, while small household induction heating equipment typically requires only a few hundred watts (W) to several kilowatts of power.
3. Stability and controllability: The power supply must provide stable current and voltage to ensure control and stability of the heating process. Induction heating systems often require highly precise current and voltage control.
4. Frequency adjustability: Some applications require the ability to adjust the operating frequency of the power supply to adapt to the requirements of different materials and workpiece sizes. Karena itu, some induction heating system power supplies have adjustable frequency capabilities.
5. Power supply efficiency: An efficient power supply can reduce energy waste and reduce operating costs. The efficiency of a power supply is usually measured in terms of power factor and conversion efficiency.
6. Keamanan: The power supply must comply with safety standards to ensure the safety of operators. This includes features such as overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and temperature protection.
7. Kemampuan beradaptasi: The power supply must adapt to the heating requirements of different materials and workpieces. Karena itu, it may need to have multiple power and frequency settings to suit different heating applications.
8. Control system integration: The power supply usually needs to be integrated with the control system of the induction heating system to realize automation and monitoring of the heating process.
Singkatnya, the power requirements for induction heating systems vary based on specific application needs and workpiece characteristics. Persyaratan ini perlu dipertimbangkan secara hati-hati ketika merancang dan memilih catu daya untuk memastikan bahwa sistem dapat beroperasi secara stabil dan efisien untuk memenuhi persyaratan proses pemanasan..
